This blog introduces the definition, work principle, types, wire amount, application and common malfunction of RTD sensor.
What Is An RTD Temperature Sensor?
RTD Sensor, Resistance Temperature Detector, can detect temperature based on a principle that the resistance value of precious metal change with the temperature. Even, it can measure as low as 800 centigrade.
The RTD Sensor comes with a platinum resistance element, a shell and an outlet wire. The platinum resistance element is the core component. The wire is used to transmit the signal. And, the shell protects the element from external influences. Therefore, it is of high precision, stability and reliability. However, it is more expensive than thermocouple temperature sensors.
How Does A Resistance Thermometer Work?
RTD Working Principle
Within the range from -200 centigrade to 850 centigrade, there is a good linear relationship between the resistance value of the platinum resistance and the temperature. Therefore, when the temperature changes, the resistance value of the platinum resistance will increase or decrease accordingly. After current passes through a platinum resistor, it creates a voltage drop at both ends. This voltage drop is proportional to the resistance value, according to Ohm’s law V=IR. Then, temperature transmitter then measures the voltage drop generated by a small current passing through the RTD Sensor. Last, the corresponding temperature value is converted by analysis.
Telecommunication Working Principle
The above analysis conversion should be operated by the processor, which will send the data to the WiFi network through the WiFi module and finally to the remote server or monitoring terminal. In this way, users can access remote servers by computers and mobile phones to get temperature data in real time. Also, it can even be integrated with smart home systems. For example, the smart air conditioner will be automatically turned on when the temperature detected by RTD reaches a preset value.
RTD Sensor Types
Thin-film RTD Sensor
The working principle of thin-film thermistor temperature sensor is thermistor effect. Specifically speaking, the thin-film thermistor material in the sensor changes its resistance value when the temperature changes.
The raw material of this film contains platinum (Pt) or nickel (Ni), as well as semiconductor materials with special thermal properties. And it is attached to a ceramic, glass or metal substrate by micro-machining technology to form a sensor element. With such a special process treatment, the film material comes with good stability, so it can maintain the measurement accuracy in harsh environments. Moreover, its relatively small size makes it easy to measure temperature in a narrow space. These advantages make thin-film RTD widely used in the field of environmental monitoring.
Wire-wound RTD Sensor
The wire-wound RTD sensor takes the advantages of the temperature-dependent resistance of a wire wound on an insulating substrate for temperature measurement. When the temperature increases, the resistance value of the metal wire increases. Conversely, when the temperature decreases, the resistance value decreases. Common winding methods of metal wire include straight rod type, threaded type, flange type to adapt to the metal wire material and insulation base. This wire-wound structure gives the sensor strong mechanical strength and durability, so it can also work stably in hard environments.
Coiled Element RTD Sensor
The Coiled Element RTD sensor is mainly composed of metal wire wound on an insulated base, which acts as the core temperature measuring part of the sensor in the form of a coil. In addition, the sensor contains components for shelling to protect internal components.
Why Does An RTD Have 3 Wires?
The design of the 3-wire is mainly to improve the accuracy of temperature measurement and anti-interference ability.
In a 3-wire RTD, there are usually three wires of equal length, material and cross-sectional area. Two of the wires, which are connected to both ends of the RTD, are used to transfer the excitation current. A third wire is connected to the middle point of the RTD or the other end of the bridge for voltage measurement. As a voltage compensation line, it effectively offset the effect of wire resistance on measurement results. Finally, combined with the known excitation current value, the sensor measures the voltage drop along the wire to obtain the resistance value and temperature of the RTD.
Last but not least, the additional wires serve as shielding or ground wires to reduce the impact of external electromagnetic interference on the measurement results.
What Is the Difference Between 2-wire, 3-wire and 4-wire RTD Temperature Sensors?
| 2-wire RTD Sensor | 3-wire RTD Sensor | 4-wire RTD Sensor | |
| Amount of Wires | 2 | 3 | 4 |
| Function of Wires | Currents transmission Voltage measurement | 2 for Currents transmission 1 for Voltage measurement | 2 for Currents transmission 2 for Voltage measurement |
| Accuracy | Low | High | Higher |
| Cost | Low | Middle | High |
| Structural Complexity | Low | Middle | High |
| Installation Difficulty | Easy | OK | Hard |
| Application | Short distance transmission No requirement of high precision | Medium distance transmission Requirement of high precision | Laboratory Scientific research |
Compared to 3-wire RTD, 2-wire RTD sensors are convenient to wire, so their manufacturing costs are relatively low. It consists of a resistance element and two lead wires. These two leads connect to each end where the RTD links to the measurement circuit. Over long distances, the effect of wire resistance on measurement results becomes more significant.
In contrast, the 4-wire type is more accurate than either of the above types. It comes with a resistance element and four lead wires. Among these four lines, two are used to transmit the excitation current, while the other two are used to measure the voltage drop at both ends of the RTD. This design separate the excitation current line and the measurement line, which eliminates measurement errors due to wire resistance.
What Is the Difference Between RTD and Thermocouples?
Thermocouples and RTDS work very differently. It is a temperature measuring element formed by welding wires of two different materials. The electromotive force (voltage) of these two materials is related to the temperature change. According to the Seebeck effect, when there is a temperature gradient at both ends, there will be an electromotive force (thermoelectric motive force) in the loop. Exactly, the thermoelectric motive force is proportional to the temperature change. In this way, the sensor can get the temperature value.
Due to their different fundamental working principles, their other properties are correspondingly different as follows.
| RTD | Thermocouples | |
| Accuracy | Good | OK |
| Stability | Good | Good |
| Temperature Range | Low to Middle Centigrade | High Temp. Several Thousand Centigrade |
| Reflection Speed | OK | Good |
| Corrosion Resistance | OK | Good |
| Cost | High | Medium |
| Application | Industrial automation control, aerospace, medical equipment | Temperature measurement in industrial heating and cooling processes, laboratory, heat treatment ,high temperature environments |
Can We Use Thermocouple Instead of RTD?
It depends. In high temperature environments, a thermocouple is usually a better choice because it is able to withstand a higher temperature range. However, for needs requiring high accuracy and stability, thermal resistors may be more suitable. If the guest is more cost sensitive, then the thermocouple will be better.
Resistance Temperature Detector (RTD) Applications
RTD Sensor for Home Automation
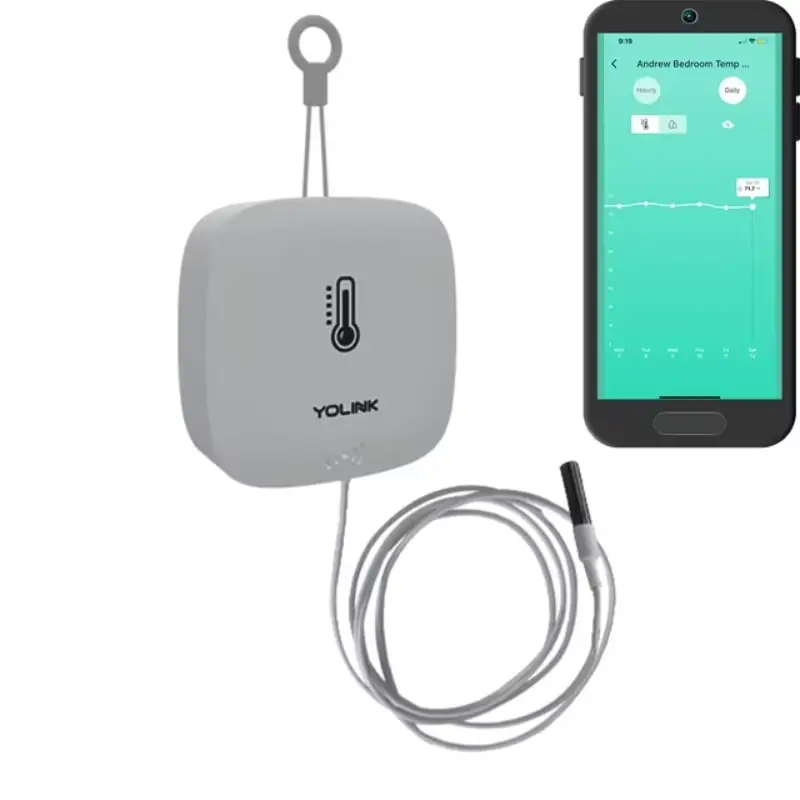

Application: Fish pond in the house, swimming pool, hot spring pool
Type: Smart Sensor Device
Network: Bluetooth/Wifi/Zigbee/+
Bridge: Need/No Need
Display Type: LCD/LED/No Display With Build-in Controller
Power source: Battery/Type C/Both/+
Waterproof: IPX4
Installation mode: Wall Hanging/Hook Hole/Table Standing/Magnetic Back
Order mode: ODM/OEM
Industrial Application
In HVAC systems, RTD sensors is for measuring indoor temperature and pipe temperature in the purpose of ensuring the normal operation of the system. In power generation equipment such as turbines and generators, RTD sensors monitor the temperature inside the equipment and prevent overheating in order to ensure the efficiency and safety of the equipment. More and more, factory production line uses RTD sensors to monitor chemical reaction temperature and fluid temperature. This aims to ensuring product quality and production efficiency.
Medical Equipment
In a thermometer, the RTD sensor can accurately measure the body temperature and thus provide important information for doctors to diagnose diseases. In addition, in some high-end medical devices, RTD sensors are also used to monitor the temperature inside the device to ensure the normal operation of the device and the safety of the patient.
Scientific Research
In weather stations, RTD sensors are used to measure ambient temperature and provide an important basis for the collection and analysis of meteorological data. Besides, chemistry laboratories apply RTD sensors in various temperature-related experiments and research.
What Causes RTD Sensor Failure?
- Improper mounting position: The mounting position of the sensor significantly affect its measurement results. If the installation position comes with strong thermal radiation, cooling effect, or insufficient contact with the measured medium, it may lead to measurement errors.
- Connection problems: If there is poor contact, short circuit, or open circuit, the RTD sensor can’t work normally.
- Drift failure: The difference between the measured value of the sensor and the true value may gradually increase over time. This may be due to the aging of the sensor, changes in material properties, or environmental factors.